Jargon is bad for communication. But there’s one word that’s hard to avoid these days: democratization. It’s a mouthful. But unlike most buzzwords — there’s meaning in it. It captures a powerful shift happening in the world of application development.
Think back 10 years ago. Only a few groups could have their technology needs met. In fact, a Deloitte report once claimed that business needs almost 5X the app the IT can deliver. Now, the situation is totally different.
Imagine a marketing manager. They can now ask for changes in an application used for managing campaigns, or even do it themselves. This change is big. It gives everyone (and we absolutely mean everyone) in an organization the power to create the tools they need. This brings us to “citizen development.” It’s a concept where creating applications isn’t limited to IT experts anymore. It’s for everyone.
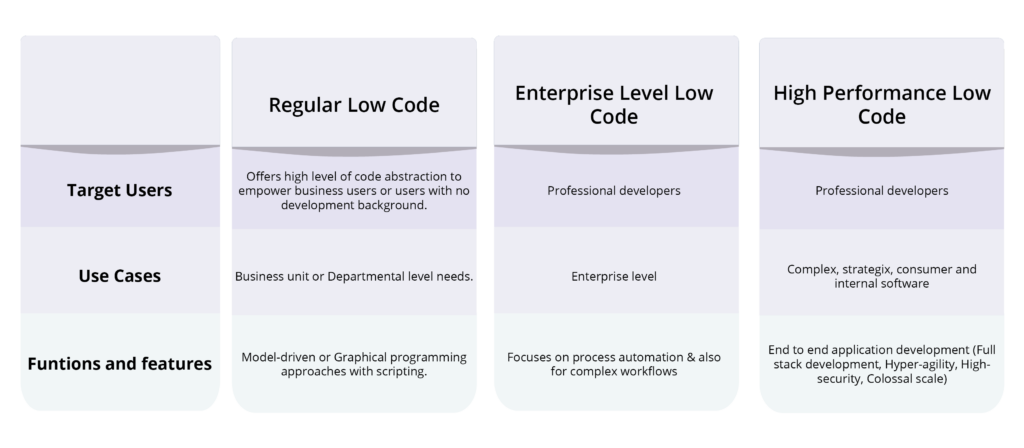
Like citizens in a democracy, citizens in an organization enjoy the same right to great tech. To understand this evolution, we need to explore three key approaches: high-code, low-code, and no-code.
1. What is high-code development?
You’re probably familiar with high-code already. It’s the traditional way to build software. It’s like the backbone of serious, heavyweight app development.
Think of teams who code in Java, Python, or JavaScript. Setting up the right environment, picking a technology stack, ensuring the best practices – all these are part of life when your team (or vendor) is trying to build a high-code application. High-Code is perfect for highly complex enterprise apps, whether for internal use or a SaaS product.
1.1 The evolution of high-code
It’s tempting to dismiss high-code as ‘that thing they used in 2005’. That is naïve.
First – High-Code has a place in a CTO arsenal, that no other development approach can take. You know the thrill of launching a feature-rich app with sleek UI/UX, tailored perfectly to business needs. That’s the beauty of High-Code – it gives you the freedom and capacity to create without boundaries.
Second – Over time, High-Code has become more efficient. There’s a whole arsenal out there – MVT frameworks, cloud services like Azure or AWS, and various development tools. Agile methodology has been a game-changer, helping CTOs get better results without burning out their teams.
But let’s talk about the elephant in the room.

Source: Forbes
Few have the courage to see the elephant in the room. The skill to tame it is even more rare.
1.2 The challenge of high-code
High-code can be a tough nut to crack. It’s expensive, time-consuming, and sometimes feels like moving mountains.
Ask a CTO what it feels like to be bogged down by the complexities of coding or managing a sprawling codebase. And technical debt – that’s a term we hear all too often. Over the years, high-code applications become a patchwork quilt of sorts.
Why?
Because knowledge transfer is hard. No single person understands the high-code app inside out. Bug fixes become myopic, trading speed for refinement. An immobile app forces users to find shortcuts to overcome the process gaps. Over time, high-code apps are prone to groan under the weight of hasty, myopic bug fixes. More than half the time isn’t spent untangling previous work rather than innovating.
Over time, small cracks and flaws start to show. Fixing these becomes a huge task, often bigger than building it right in the first place. For companies, technical debt slows down new developments, creates security risks, and can even lead to customer dissatisfaction. It’s like carrying a heavy backpack on a long hike – it slows you down and makes every step harder. This forces CTOs to stare right into the eye of a scary question.
1.3 Can high-code adapt to agile business needs
This is what every tech leader asks: How can we keep up with the pace of business today with High-Code? It’s a challenge when you need to be agile but are tied down by traditional coding. That’s the trade-off with High-Code. Back in the day, it was like the Ferrari of application development — if you could afford it and then maintain it. Unmatched power, unparalleled flexibility, and features that could make your competitors drool. But just like maintaining a Formula One race car — at what cost?
Again, let us not for a moment let you assume that we’re deriding high-code. It’s all we had a decade ago. But today, a CTO’s options are many. One end of the spectrum is high-code, and on the other… no-code. It’s like going from ‘maximum flexibility and very little convenience’ to ‘limited scope but absolute convenience’.
The problem is obvious: nobody wants extremes. So before we get to know ‘no-code’ better, let’s learn about the balanced approach, called ‘low-code’.
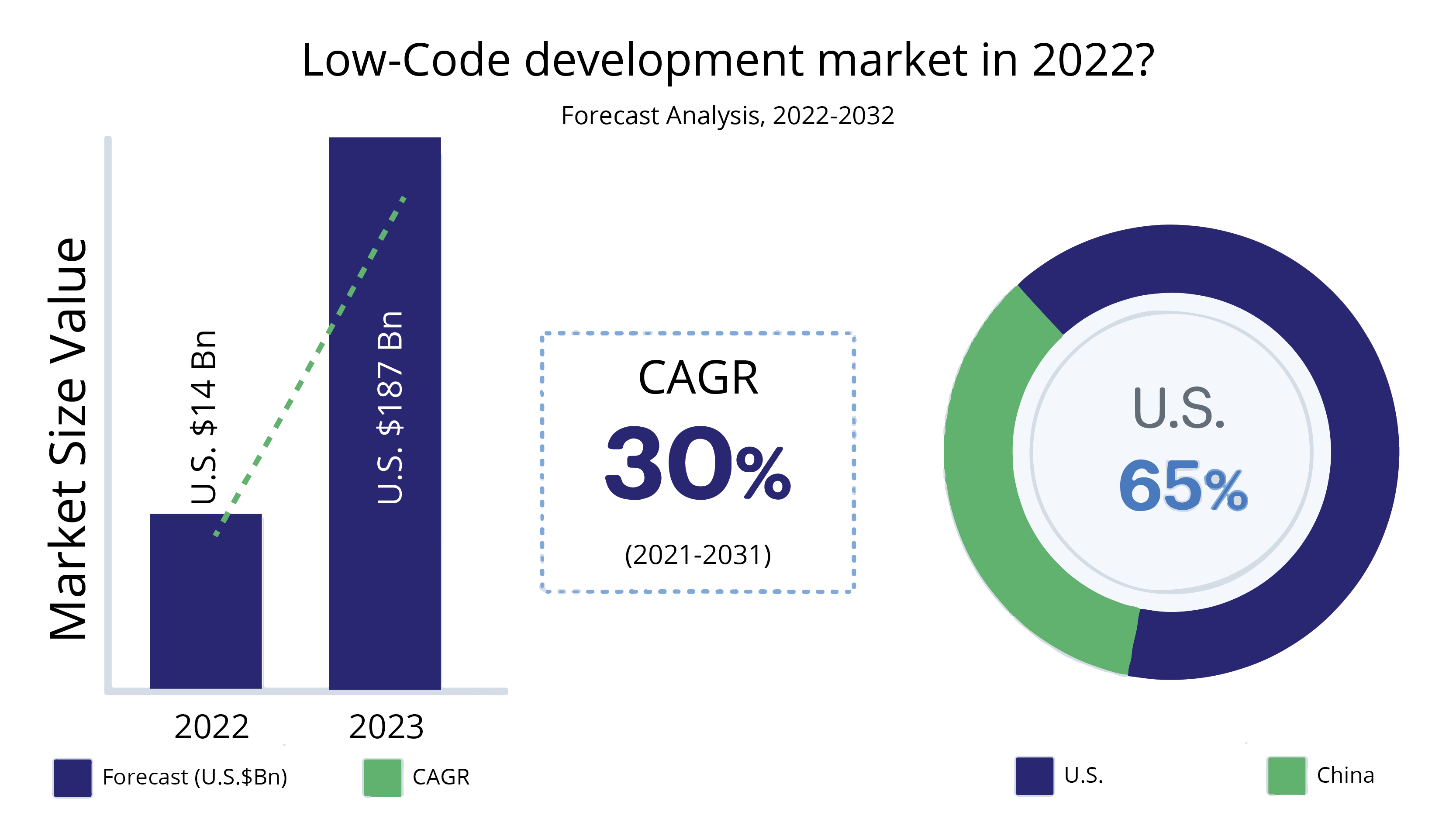
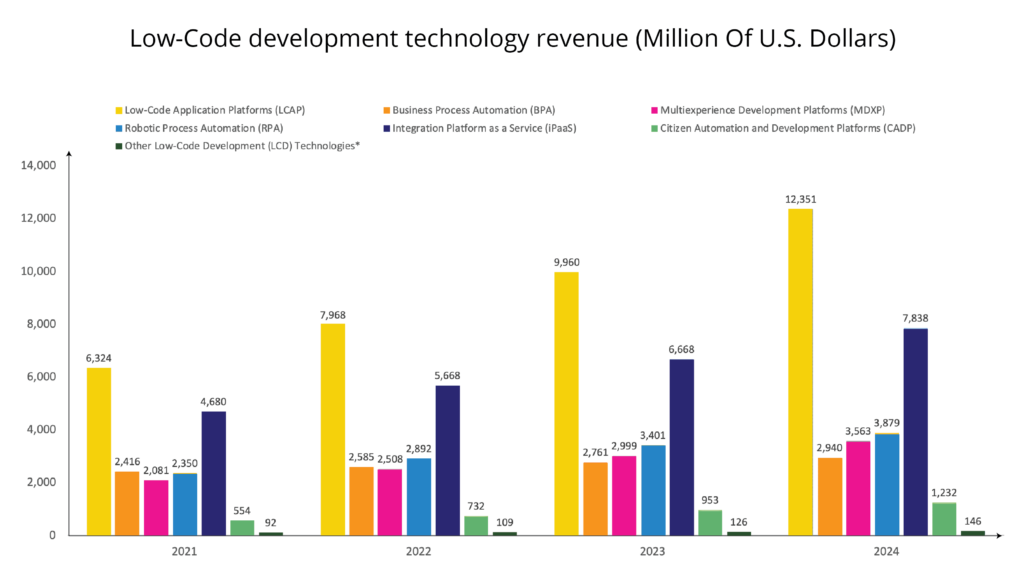
2. What is Low-Code Development?
Low-code development rethinks traditional coding. It offers a simpler, more visual way of building applications.
How does that happen?
It’s a bit like using a mix of pre-made templates and your own custom designs to create a website. You use tools like drag-and-drop interfaces, which make the process faster and easier, but you can still add your own code for more complex features. More specifically, a user of a low-code development platform will see ‘modules’ like a drag-and-drop interface, templates, widgets, connectors, and visual workflow diagrams. They will ‘build’ the desired app, and as they use the blocks, the code is auto-generated in the backend.
2.1 Low-code is the best of both worlds
Low-code is perfect for creating business software, websites, and mobile apps. It’s simple enough for a non-techie to use, and powerful enough to even work seamlessly with any other application using APIs. It’s like having the best of both worlds — ease, and power. Users enjoy the flexibility to customize apps needed while keeping the process straightforward and accessible. But the best part about low-code is that it simply ‘abstracts’ (hides) the complications of coding, but retains the facility to let a coder jump in and make an application do anything, just like they would in a high-code platform.
Let’s understand this in more detail.
2.2 The role of citizen and low-code developer
Low-Code has given birth to two key roles in organizations: the citizen developer and the low-code developer. The citizen developer could be anyone from your team, engaging in app development. They’re not just suggesting ideas; they’re actively involved in the design and development, just because it is so easy to build an app. While any citizen developer can use a low-code development platform, there still is room for what you might call a ‘low-code app developer’. You could have them in-house. Better still, the low-code platform you choose might also offer low-code app development services, which cost 1/10th of traditional development, and are about 4 times as fast.
Consider the example of WordPress used by marketing teams. They can start with a template, making significant changes without needing technical support. But for more intricate features, they turn to a low-code developer, who combines technical expertise with a sense of design. We took the example of WordPress because it’s familiar. low-code is as good for website development as it is for building a CRM.
2.3 Low-code can do more than you think
The low-code platform of today is so powerful, it’s surprising if you’ve not tracked the evolution for even the last two years. Low-Code is reliable enough to automate entire operations, including CRM, ERP, and workflow management. It’s not just faster; it’s cost-effective too – often 10 times faster and a quarter of the cost compared to traditional coding.
If you’re thinking, ‘Hang on a minute; this is a new way of thinking about app development,’ you’re right. It’s a blend of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and business agility, of the type not known to technology leaders who never looked beyond high-code.
Now, let’s look at no-code development.
3. What is No-Code Development?
No-code is a term that rolls off the tongue. You’d be surprised how every development platform claims to be either a ‘low-code’ or a ‘no-code’ platform, which in reality is merely a high-code platform with GUI-based configurations built on top. But that’s a matter for another day. For the moment, let’s find out more about low-code.
No-code development is like using building blocks to create applications, but without needing to write any code. It’s a step beyond (not truly beyond, but let’s say it’s a step aside) low-code development, which still requires some coding.
With no code, everything is visual. You just drag and drop elements to build your app. You don’t need to know design or programming; you just pick what you need and put it together. This approach is great for simple projects like business apps, dashboards, websites, and even tools for managing calendars or reports.
3.1 Examples of no-code
A familiar example of a no-code app that many people use is Google Forms. This tool allows users to easily create surveys, quizzes, and forms without any programming knowledge. It offers a simple drag-and-drop interface for adding questions and customizing form elements. Anybody can use it with ease.
Another prominent example of a no-code app is Wix. It is a popular web development platform that allows users to create websites using a drag-and-drop interface, with no need for coding. It’s designed for ease of use and lets users select from a variety of templates and then customize their site with intuitive tools.
Let’s consider another example – something more familiar. Consider MS Excel. For many, it’s a straightforward spreadsheet tool. We’d say most people think of it as a no-code tool. But it’s not. MS Excel also offers advanced features like macro writing and .NET programming, which venture into the realm of Low-Code for those who use them. This dual nature makes Excel a unique example – it’s actually low-code, but familiar to most as no-code.
3.2 Limitations of no-code
No-Code has its boundaries. These platforms excel at straightforward applications but often fall short in more complex scenarios. Teams are forced to improvise when a No-Code app doesn’t quite fit the bill. They might add manual steps or juggle between multiple tools. That’s because No-Code isn’t designed for the heavy lifting of enterprise-grade automation.
Aspects like robust security, detailed access control, and comprehensive integration – remain out of reach for most No-Code solutions. So, where does no-code find its rightful place in your app development artillery?
It shines in prototyping, building internal tools, or iterating on simple user interfaces. If that’s enough for your team, then No-Code is enough. But the question isn’t as much ‘which one to choose between high-code and low-code and no-code’ as much as it’s ‘when to use which’.
4. How to Choose Between High, Low, and No-Code?
To choose the right development path – high-code, low-code, no-code – you need a clear understanding of your project’s needs and limitations.
Ask yourself these key questions:
How complex is my project?
Choose low-code for user-specific functionalities or streamlined internal tools. High-code suits projects needing a large IT team.
What’s my development timeframe?
No-code or low-code is ideal for rapid prototypes or MVPs. High-code is better for longer, customized development.
What level of technical expertise will I need?
High-Code requires skilled developers. Low-code is suitable if you want to enable non-technical users or need a balance of skills and speed.
What is my budget?
High-Code demands more resources and investment. Low-code or no-code is more cost-effective for simpler applications or rapid prototyping.
Will my applications need to evolve?
Consider Low-Code for scalable solutions that can evolve with your business needs. High-Code is needed for highly scalable and complex systems.
Remember, each approach has its trade-offs. By honestly answering these questions, you’ll gain a clearer picture of your project’s landscape and find the development path that best suits your needs, resources, and goals. Often, it’s hard to give definitive answers to these questions.
That’s when CTOs wish for a platform that:
- balances the maturity of high-code and user-friendliness of no-code
- offers all the advantages of low-code
- allows low-code developers to step in when needed, to deal with complex requirements
Some low-code development platforms tick these three boxes. Amoga is one of them.
Here’s more.
Low-Code with Amoga: Control Meets Agility
Amoga is best imagined as the toolbox of an expert builder, but for making apps. It’s filled with ready-to-use parts and tools that are easy to handle. With Amoga, you can put together powerful applications quickly, without losing the ability to make them just how you want.
Here’s how Amoga can be a game changer for your business:
- Balancing control with agility: Amoga lets you build complex, professional apps. You get the precision of advanced coding, but it’s as quick and easy as simpler methods.
- Speedy development: Create apps up to 10 times faster than the old ways. This means you can offer new value to your customers much sooner.
- Empowering everyone: Even if you’re not a tech expert, you can build solutions with Amoga. This frees up your IT team for more big-picture projects.
- Easy connections: Amoga fits smoothly with your existing systems and data, creating a unified digital world for your business.
- Top-notch security: With Amoga, your apps and data are safe, meeting the highest industry standards.
By choosing Amoga, you will:
- Cut down costs: Save on resources and get your products to market faster.
- Boost efficiency: Automate routine tasks, streamline your operations and improve overall productivity.
- Improve customer experiences: Offer personalized, user-friendly apps that keep up with changing needs.
- Encourage creativity: Give your teams the freedom to try new things, refine their ideas, and quickly bring solutions to life, all of which can lead to business growth and flexibility.
There’s nothing better than a conversation; let us hear your experiences with app development. Let’s tell you — no, let’s show you — what’s possible with Amoga.
Contact us today.